

A single snail can produce up to 4,000 cercariae. Once inside the snail, larvae develop and multiply as sporocysts, rediae and cercariae. It lives in various habitats and its range is expanding. A third host snail, Radix viridis – has been introduced from the Pacific Islands (Guam). In coastal subtropical Queensland and NSW, the exotic snail Pseudosuccinea ( Lymnaea) columella has become endemic and is known to transmit liver fluke.
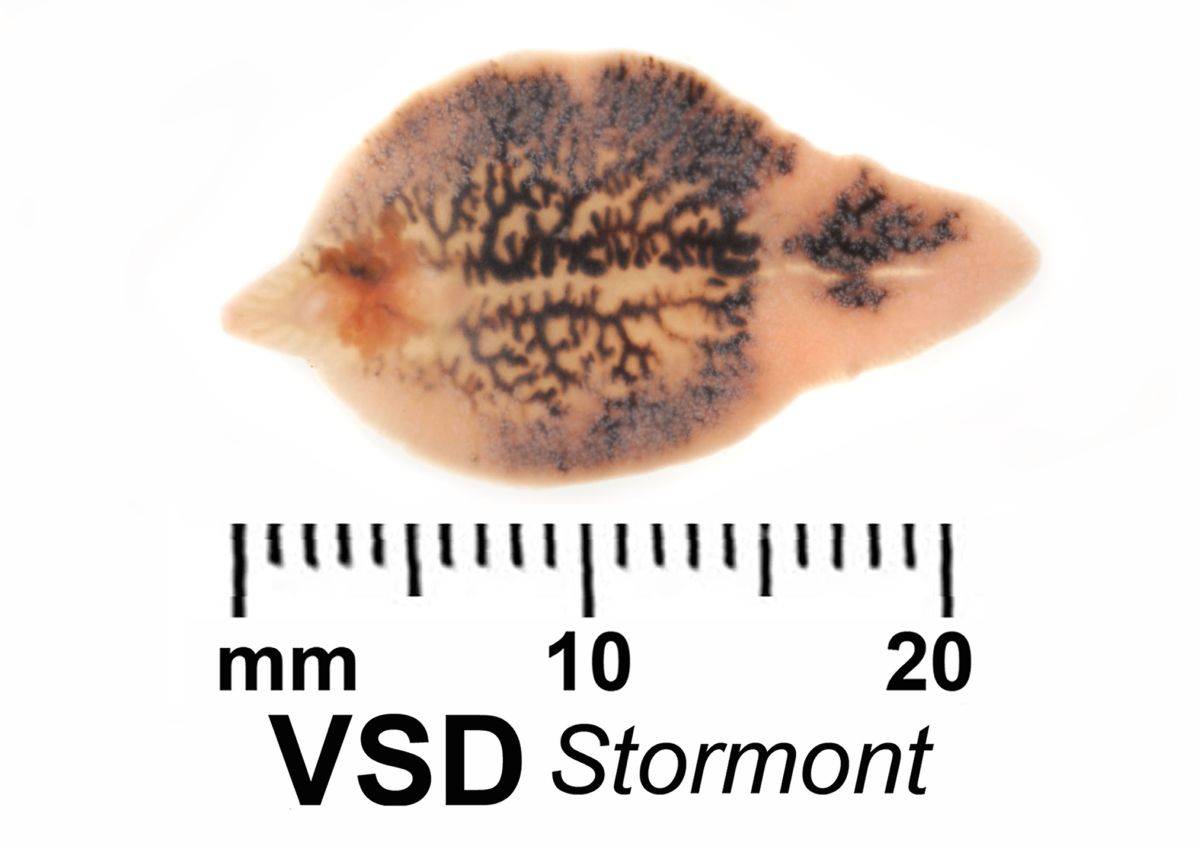
Larvae (miracidia) invade the intermediate hosts, which are aquatic lymnaeid snails: most commonly Austropeplea ( Lymnaea) tomentosa in southern Australia and New Zealand. The eggs hatch in wet areas on pasture when mean daily temperatures are over 10☌. Life cycleĪdult fluke in bile ducts produce eggs that flow in the bile to the intestines and are passed out in the host’s faeces. Liver fluke may also be found in irrigation areas and also coastal areas of Queensland. Liver fluke is limited to the higher rainfall (>600 mm per year) areas of NSW (typically the tablelands in the eastern part of the state, and nearby coastal areas to the east and slopes to the west), Victoria and Tasmania, and to small areas in Queensland and South Australia. Liver fluke occurs in regions and areas on individual farms where watery environments, such as springs, slow-moving streams with marshy banks, irrigation channels and seepages, suit hatching of fluke eggs into swimming larvae and provide a habitat for aquatic snails. Source: Bruce Watt Central Tablelands LLS Distribution of liver fluke As with many worms, most of the economic cost is associated with production losses from infections that may not be apparent.Īdult liver fluke (marked x) on cut surface of liver. Liver fluke costs millions of dollars each year in lost production, stock deaths, and costs of treatment and prevention.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
